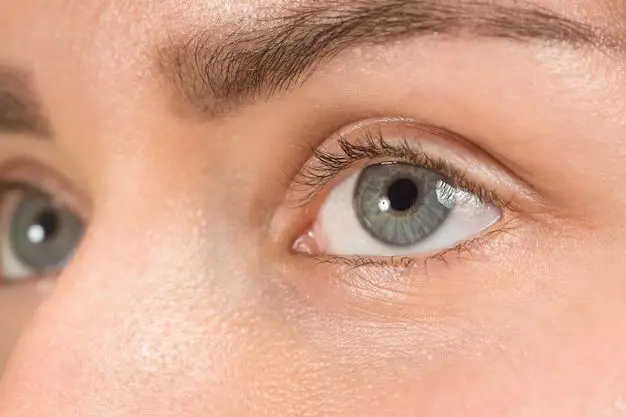
Grey eyes are one of the most fascinating and rare eye colors. Unlike blue, brown, hazel or green eyes that have higher levels of melanin, grey eyes contain low to moderate amounts of melanin in the iris. This results in grey, blue, or greenish hues that can shift between colors in different lighting conditions. But what exactly qualifies as true grey eyes? Let’s explore the key factors that make grey eyes so unique.
The Science Behind Grey Eyes
The color of our eyes is determined by the amount and type of melanin in the iris. Melanin is a pigment that gives color to our hair, skin and eyes. There are two types of melanin:
– Eumelanin: A brown/black pigment. Eyes with high levels appear brown or black.
– Pheomelanin: A red/yellow pigment. Eyes with high levels appear blue or green.
Grey eyes have low to moderate concentrations of both eumelanin and pheomelanin. This pheomelanin concentration also gives grey eyes a blue or greenish tinge based on lighting conditions. The exact genetics behind grey eyes are still being researched, but it appears to be a rare result of the OCA2 gene.
Defining Features of True Grey Eyes
So what are the key features that set grey eyes apart from other colors? Here are the defining characteristics:
1. Low melanin levels
As discussed above, low to moderate melanin concentration is what creates the greyish color. The less melanin present, the lighter the grey hue will appear.
2. Blue/green hues
While some grey eyes may appear slightly brown, most commonly they exhibit blue, green, silver, or aquamarine hues. This is caused by the pheomelanin concentrations.
3. Changeable color
One of the most distinguishing features of grey eyes is how the color can drastically shift between blue, green, hazel and brown depending on lighting conditions. Bright lighting brings out the blue hues, while dim lighting leads to a darker, grey-brown shade.
| Lighting Condition | Eye Color |
|---|---|
| Bright sunlight | Ice blue |
| Cloudy daylight | Blue-grey |
| Indoor lighting | Green-grey |
| Dim lighting | Brown-grey |
As you can see, grey eyes are like chameleons that can transform between shades.
4. Distinct grey ring around the pupil
Look closely at a grey eyed person, and you’ll notice a pronounced grey or blueish ring outlining the pupil. This ring distinguishes them from other light eye colors.
5. Rarity
Only around 2% of the world’s population has true grey eyes. This rare genetic combination helps classify grey as a distinct eye color group.
Comparison to Blue and Green Eyes
How are grey eyes different from blue and green? While it’s true that grey eyes exhibit blue and green hues, they are distinct in the following ways:
Blue Eyes
– Richer, deeper blue tone
– Less melanin than grey eyes
– More consistently blue rather than changeable
– No outer grey ring around pupil
Green Eyes
– Distinct green hue with no grey
– Higher melanin than grey eyes
– Grass green, emerald green or hazel green shades
– No outer grey ring around pupil
So in summary, grey eyes are set apart by their lighter, desaturated grey-blue-green color, outer ring, and chameleon-like ability to shift between shades. They cannot be classified as strictly blue or green.
Conclusion
Grey eyes are a rare and stunning eye color that occur when people have low levels of both melanin pigments. The combination of eumelanin and pheomelanin produces alluring hues of blue, green and grey that can change with lighting conditions. Key identifying features include a pale greyish color, distinct outer ring, blue/green tinges, low melanin, and the chameleon-like ability to transform between shades. Only 2% of people in the world have these exquisite charcoal gemstones for eyes. So if you have true grey eyes, be sure to flaunt these brilliant optical jewels!